Russia Ukraine War and NATO Connection
Russia Ukraine War and NATO Connection
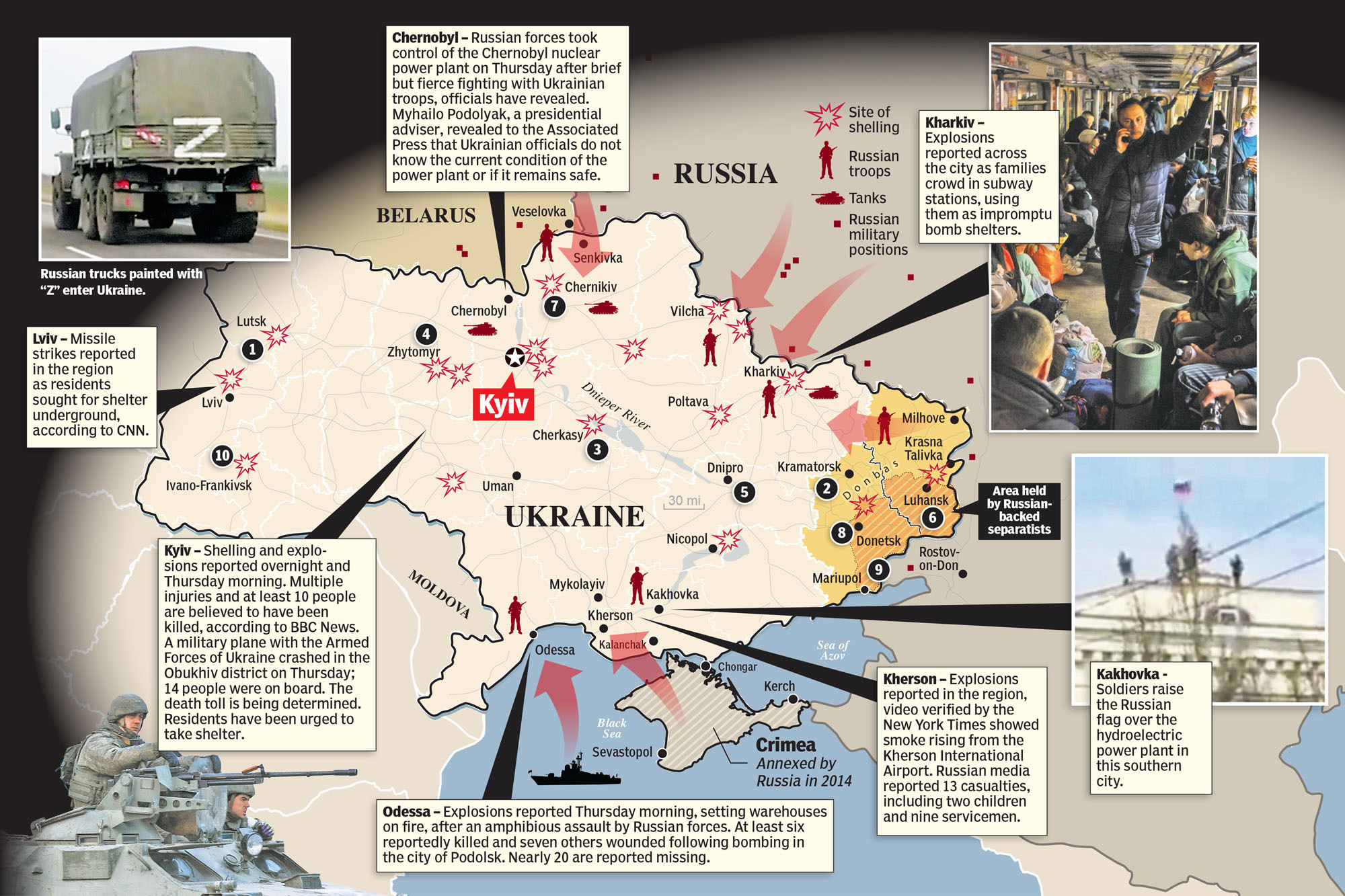
Russia’s unjustifiable incursion into Ukraine following weeks of military troop build-up on their shared border has drastically raised tensions in the region with broader ripple effects across the world, particularly for NATO countries and others with strategic connections to the two nations.
What is NATO?
1. The North Atlantic Treaty Organization was founded ‘in response to the threat posed by the Soviet Union.
2. It implements the North Atlantic Treaty, signed on April 4, 1949. On singing the Treaty, countries voluntarily commit themselves to participating in the political consultations and military activities of the Organization.
3. In 1949, there were 12 founding members of the Alliance. The end of the Cold War opened up the possibility of further NATO enlargement.
4. 40 non-member countries work with NATO on a wide range of political and security-related issues.
Why Russia attacked Ukraine
1. At the 2008 Bucharest Summit, Allies agreed that Georgia and Ukraine will become members of NATO in future.
2. As of 2020, three partner countries have declared their aspirations to NATO membership Bosnia and Herzegovina, Georgia and Ukraine.
3. Ukraine has cooperated with the alliance and frequently expressed its intention to sign up. Russia believes Ukraine is moving closer to the West via the NATO and the European Union.
4. Russia President Vladimir Putin was aware Ukraine joining NATO would significantly increase the difficulty of bringing Donetsk and Luhansk within his control.
How is Russia violating the UN Charter?
1. Russia launched a full-scale invasion on Ukraine. The Russian actions have been widely condemned and raise several questions concerning violation of international law.
2. The principle of non-intervention is enshrined in article 2(4) of the UN Charter. It requires states to refrain from using force or threat of using force against territorial integrity or political independence of any state. The Russian attack on Ukraine is violative of this principle, and amounts to aggression under international law. Russia’s desire to keep Ukraine out of NATO is a prime reason for its use of force against Ukraine.
3. Russia has claimed it is acting in self-defence as Ukraine could acquire nuclear weapons with the help of its western allies. However, the International Court of Justice in the Legality of Threat of Nuclear Weapons case held that mere possession of nuclear weapons does not constitute a threat. Further, mere membership in a defence alliance like NATO can also not be considered a threat of aggression.
30 NATO member countries:
1. ALBANIA (2009)
2. BELGIUM (1949)
3. BULGARIA (2004)
4. CANADA (1949)
5. CROATIA (2009)
6. CZECH REPUBLIC (1999)
7. DENMARK (1949)
8. ESTONIA (2004)
9. FRANCE (1949)
10. GERMANY (1955)
11. GREECE (1952)
12. HUNGARY (1999)
13. ICELAND (1949)
14. ITALY (1949)
14. LATVIA (2004)
16. LITHUANIA (2004)
17. LUXEMBOURG (1949)
18. MONTENEGRO (2017)
19. NETHERLANDS (1949)
20. NORTH MACEDONIA (2020)
21. NORWAY (1949)
22. POLAND (1999)
23. PORTUGAL (1949)
24. ROMANIA (2004)
25. SLOVAKIA (2004)
26. SLOVENIA (2004)
27. SPAIN (1982)
28. TURKEY (1952)
29. THE UNITED KINGDOM (1949)
30. THE UNITED STATES (1949)